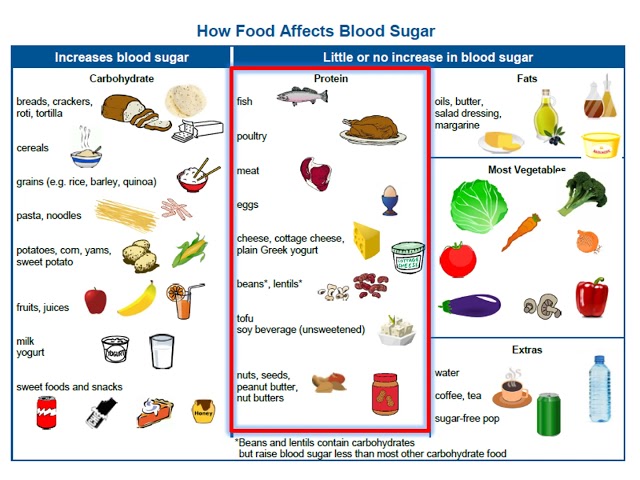
Foods diabetics can eat are foods that are low in carbohydrates and sugar. This is because carbohydrates and sugar can raise blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous for people with diabetes. There are many different types of foods that diabetics can eat, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. These foods help to keep blood sugar levels stable and provide essential nutrients.
Eating a healthy diet is important for everyone, but it is especially important for people with diabetes. A healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall health and well-being.
If you have diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian about what foods you should eat. They can help you create a meal plan that is right for you.
Foods Diabetics Can Eat
For people with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial. Consuming appropriate foods forms a cornerstone of this management strategy. Here are six key aspects to consider when selecting foods for diabetics:
- Glycemic index: This measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels.
- Carbohydrate content: Carbohydrates are broken down into sugar in the body, so diabetics need to be mindful of their intake.
- Fiber content: Fiber helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
- Protein content: Protein can help to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Fat content: Healthy fats can help to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, but saturated and trans fats should be limited.
- Portion size: Eating smaller portions can help to control blood sugar levels.
Understanding these aspects and making informed choices about the foods they consume empowers diabetics to manage their condition effectively. For instance, opting for foods with a low glycemic index, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help prevent blood sugar spikes. Incorporating fiber-rich foods, like beans, lentils, and oatmeal, aids in regulating blood sugar levels. Including lean protein sources, such as fish, chicken, and tofu, helps stabilize blood sugar and promotes satiety. By considering these aspects, diabetics can make dietary choices that support their overall health and well-being.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a sharp rise in blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels.For people with diabetes, it is important to choose foods with a low GI. This helps to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevents spikes. Some examples of low-GI foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beans.Here are some of the benefits of choosing low-GI foods for people with diabetes:
- Helps to keep blood sugar levels stable
- Prevents spikes in blood sugar levels
- Reduces the risk of developing complications of diabetes
If you have diabetes, talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian about how to incorporate low-GI foods into your diet.
Carbohydrate content
Carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that provides the body with energy. However, for people with diabetes, managing carbohydrate intake is crucial to control blood sugar levels. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into sugar, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous for people with diabetes.
To manage blood sugar levels, diabetics need to be mindful of the amount and type of carbohydrates they consume. Complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested more slowly and have a lower impact on blood sugar levels than simple carbohydrates, such as those found in candy, sugary drinks, and white bread. It is important to note that even healthy carbohydrates should be consumed in moderation.
In addition to considering the type of carbohydrates consumed, diabetics should also pay attention to portion sizes. Eating smaller portions can help to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. It is also important to spread carbohydrate intake throughout the day, rather than consuming all carbohydrates at one meal.
By understanding the connection between carbohydrate content and blood sugar levels, diabetics can make informed choices about the foods they eat. This knowledge is essential for managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications of diabetes.
Fiber content
Individuals with diabetes must carefully manage their blood sugar levels, and consuming foods rich in fiber is a crucial aspect of this management strategy. Fiber, a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest, plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels.
- Slows glucose absorption: Fiber forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, which delays the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. This helps prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after meals.
- Promotes satiety: Fiber promotes a feeling of fullness, which can help individuals with diabetes avoid overeating and excessive calorie intake. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing diabetes.
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Soluble fiber, a type of fiber found in oats, beans, and apples, has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which is the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
- Reduces cholesterol levels: Some types of fiber, such as soluble fiber, can bind to cholesterol in the digestive tract and prevent its absorption into the bloodstream. This can help reduce cholesterol levels, which is important for heart health.
Incorporating fiber-rich foods into the diet is essential for individuals with diabetes. By slowing down the absorption of sugar, promoting satiety, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing cholesterol levels, fiber helps manage blood sugar levels and promotes overall health and well-being.
Protein content
Individuals with diabetes must carefully manage their blood sugar levels to maintain good health and prevent complications. Consuming foods rich in protein is an essential aspect of diabetes management, as protein plays a crucial role in stabilizing blood sugar levels.
After consuming a meal, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This process can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous for people with diabetes. Protein, on the other hand, is digested and absorbed more slowly, which helps to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
In addition, protein helps to promote satiety, which can help individuals with diabetes avoid overeating and excessive calorie intake. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing diabetes, as obesity can worsen insulin resistance and make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels.
Good sources of protein for people with diabetes include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu. Including these foods in a balanced diet can help to stabilize blood sugar levels, promote satiety, and support overall health and well-being.
It is important to note that individuals with diabetes should consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of protein to consume each day. Excessive protein intake can put a strain on the kidneys, so it is essential to consume protein in moderation as part of a healthy overall diet.
Fat content
Individuals with diabetes must carefully manage their blood sugar levels to maintain good health and prevent complications. Consuming foods with the right fat content is an essential aspect of diabetes management, as different types of fats have varying effects on blood sugar levels.
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can help to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. This is because these fats form a barrier around the food, which delays the release of glucose into the bloodstream. This helps to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after meals.
In contrast, saturated and trans fats can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, which can increase the risk of heart disease. Additionally, saturated and trans fats can contribute to weight gain, which can worsen insulin resistance and make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels.
Therefore, individuals with diabetes should choose foods that are low in saturated and trans fats and high in healthy fats. Good sources of healthy fats include olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. Including these foods in a balanced diet can help to stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and promote overall health and well-being.
It is important to note that individuals with diabetes should consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of fat to consume each day. Excessive fat intake can lead to weight gain and other health problems, so it is essential to consume fat in moderation as part of a healthy overall diet.
Portion size
Individuals with diabetes must carefully manage their blood sugar levels to maintain good health and prevent complications. Consuming foods in appropriate portion sizes is an essential aspect of diabetes management, as portion size plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels.
- Reduced calorie intake: Consuming smaller portions helps reduce overall calorie intake, which is essential for weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for individuals with diabetes, as obesity can worsen insulin resistance and make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels.
- Slower glucose absorption: Eating smaller meals more frequently can help slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. This helps prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after meals and promotes better overall blood sugar control.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding excessive calorie intake can improve insulin sensitivity, which is the body’s ability to use insulin effectively. Improved insulin sensitivity helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing complications.
- Reduced risk of complications: Managing blood sugar levels through appropriate portion control can help reduce the risk of developing long-term complications of diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and eye problems.
Incorporating portion control into a healthy diet is essential for individuals with diabetes. By consuming smaller portions, individuals can manage their weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of developing complications. It is important to note that individuals with diabetes should consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate portion sizes for their individual needs.
FAQs on Foods Diabetics Can Eat
This section addresses common questions and concerns regarding the dietary needs of individuals with diabetes, providing clear and informative answers to guide their food choices and improve their overall health.
Question 1: What types of foods should diabetics prioritize in their diet?
Diabetics should focus on consuming foods low in carbohydrates and sugar, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. These foods help regulate blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients.
Question 2: How does the glycemic index impact blood sugar levels in diabetics?
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Diabetics should choose foods with a low GI to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
Question 3: Why is fiber important for diabetics?
Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and promote satiety. Soluble fiber, in particular, improves insulin sensitivity.
Question 4: How does protein affect blood sugar levels in diabetics?
Protein helps stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down digestion and absorption. It also promotes satiety, reducing the risk of overeating and excessive calorie intake.
Question 5: What is the recommended portion size for diabetics?
Consuming smaller portions helps control calorie intake, slows glucose absorption, and improves insulin sensitivity. Diabetics should consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine appropriate portion sizes.
Question 6: How can diabetics make healthy food choices while dining out?
When dining out, diabetics should consider the glycemic index of foods, opt for lean protein and fiber-rich options, and request smaller portions. They should also be mindful of hidden sugars and carbohydrates in sauces and beverages.
In conclusion, understanding the specific dietary needs associated with diabetes empowers individuals to make informed food choices that support their overall health and well-being.
Proceed to the next section for further insights on managing diabetes through dietary modifications and lifestyle changes.
Tips for Managing Diabetes Through Dietary Choices
Individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition by adopting mindful eating habits. Here are several practical tips to guide their dietary choices:
Tip 1: Prioritize Low-Glycemic-Index Foods
Choosing foods with a low glycemic index (GI) helps prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. These foods are digested and absorbed slowly, ensuring a gradual rise in blood sugar. Examples include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Tip 2: Include Fiber-Rich Options
Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, promoting stable blood sugar levels and satiety. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats and beans, can also improve insulin sensitivity.
Tip 3: Opt for Lean Protein Sources
Protein helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down digestion and reducing hunger cues. Lean protein sources, such as fish, chicken, and tofu, are recommended for diabetics.
Tip 4: Manage Portion Sizes
Consuming smaller portions helps control calorie intake, prevents overeating, and improves blood sugar control. Diabetics should be mindful of portion sizes and use smaller plates to avoid excessive consumption.
Tip 5: Choose Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and avocados, can help slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. However, saturated and trans fats should be limited as they can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Tip 6: Read Food Labels Carefully
Paying attention to food labels is essential for diabetics. They should check the carbohydrate content, sugar content, and serving size to make informed choices and manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Tip 7: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Regular blood sugar monitoring helps diabetics track the impact of their dietary choices on their blood sugar levels. This information can guide them in making necessary adjustments to their diet and lifestyle.
By following these tips, individuals with diabetes can make positive dietary changes that support their overall health and well-being.
Proceed to the next section for further insights on managing diabetes through lifestyle modifications and seeking professional guidance.
Conclusion
Individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition through mindful eating habits. By prioritizing low-glycemic-index foods, incorporating fiber-rich options, opting for lean protein sources, managing portion sizes, and choosing healthy fats, diabetics can regulate their blood sugar levels and improve their overall health.
Understanding the glycemic index, the role of fiber and protein, and the importance of portion control empowers diabetics to make informed dietary choices. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels provides valuable insights into the impact of these choices, enabling individuals to adjust their eating plans as needed.
Making these dietary modifications can significantly improve the quality of life for diabetics. By adopting these healthy habits, individuals can reduce the risk of developing complications, maintain a healthy weight, and enjoy a fulfilling and active lifestyle. It is important to seek guidance from healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians, to develop a personalized plan that meets individual needs and goals.
Youtube Video: