Complications of diabetes refer to the various health issues that can arise due to diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. These complications can affect multiple organs and systems in the body, potentially leading to severe health consequences.
Managing blood sugar levels and adhering to treatment plans are crucial for preventing or delaying the onset of these complications. Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medications are essential aspects of diabetes management to minimize the risk of developing complications.
The main article will delve into the specific types of complications associated with diabetes, exploring their symptoms, causes, and potential treatments. It will also emphasize the significance of early detection, preventive measures, and ongoing management strategies to improve outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Complications of Diabetes
Complications of diabetes are a serious concern, as they can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. Understanding the key aspects of these complications is essential for effective management and prevention.
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Nephropathy: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to blindness.
- Neuropathy: Diabetes can damage the nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness.
- Foot ulcers: Diabetes can cause poor circulation and nerve damage in the feet, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
- Gestational diabetes: Diabetes that develops during pregnancy can pose risks to both the mother and the baby.
- Type 2 diabetes: The most common type of diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
These key aspects highlight the diverse range of complications associated with diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications are crucial for minimizing the risk of developing these complications and improving the overall health and well-being of individuals with diabetes.
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease is a major complication of diabetes, significantly increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and promote the formation of blood clots, leading to a higher likelihood of these cardiovascular events.
Understanding the connection between cardiovascular disease and diabetes is crucial for effective management and prevention. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet, are essential for minimizing the risk of developing cardiovascular complications.
Early detection and intervention are key to managing cardiovascular disease in individuals with diabetes. Regular check-ups, including blood pressure and cholesterol screenings, can help identify and address any underlying issues promptly. Medications may be prescribed to manage blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Nephropathy
Nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to kidney failure. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, which can reduce blood flow and cause the kidneys to not work properly. Over time, this can lead to kidney failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
- Glomerular damage: Diabetes can damage the glomeruli, which are small filters in the kidneys that help remove waste from the blood. This can lead to proteinuria, which is the presence of protein in the urine, and can be a sign of kidney damage.
- Tubular damage: Diabetes can also damage the tubules, which are small tubes in the kidneys that help reabsorb water and nutrients from the urine. This can lead to polyuria, which is excessive urination, and can also be a sign of kidney damage.
- Interstitial damage: Diabetes can also damage the interstitium, which is the tissue that surrounds the glomeruli and tubules. This can lead to scarring and inflammation, which can further damage the kidneys.
- Hypertension: Diabetes can also lead to hypertension, or high blood pressure. This can further damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure.
Nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes, and it is important to manage blood sugar levels and blood pressure to reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Retinopathy
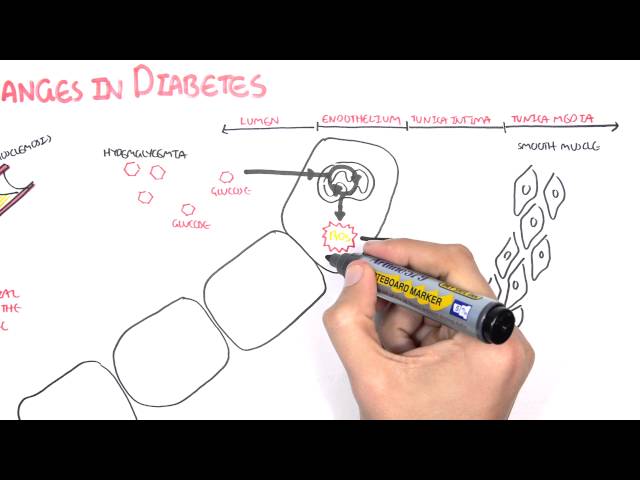
Retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This damage can cause the blood vessels to leak fluid and blood, which can lead to swelling and scarring of the retina. Over time, this can lead to vision loss and blindness.
Retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes, and it is important to manage blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of developing this condition. Regular eye exams are also important for detecting retinopathy early so that treatment can be started to prevent vision loss.
There are several treatments available for retinopathy, including laser therapy, injections of anti-VEGF drugs, and surgery. These treatments can help to stop or slow the progression of retinopathy and prevent vision loss.
Retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be managed with proper care. Regular eye exams and blood sugar control are essential for preventing vision loss and maintaining good eye health.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that can affect the nerves throughout the body. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the small blood vessels that supply the nerves. This damage can lead to a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and weakness.
- Sensory neuropathy affects the nerves that transmit sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature. Symptoms can include numbness, tingling, and burning pain in the hands, feet, and legs.
- Motor neuropathy affects the nerves that control movement. Symptoms can include weakness, difficulty walking, and problems with balance.
- Autonomic neuropathy affects the nerves that control involuntary functions such as digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure. Symptoms can include constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, and erectile dysfunction.
Neuropathy can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It can make it difficult to perform everyday activities, such as walking, eating, and sleeping. In severe cases, neuropathy can lead to disability.
There is no cure for neuropathy, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms. These treatments may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Foot ulcers
Foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to infection, amputation, and even death. Diabetes can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, which can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage. This can make it difficult for the feet to heal properly, and even minor injuries can become serious infections.
- Poor circulation: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the feet, which can lead to poor circulation. This can make it difficult for the feet to get the oxygen and nutrients they need to stay healthy.
- Nerve damage: Diabetes can also damage the nerves in the feet, which can lead to nerve damage. This can make it difficult for the feet to feel pain, temperature, and other sensations. As a result, people with diabetes may not notice injuries to their feet, which can lead to serious infections.
- Foot ulcers: Foot ulcers are open sores on the feet that can be caused by diabetes. Foot ulcers can become infected, and they can be difficult to heal. In severe cases, foot ulcers may need to be amputated.
- Amputation: Amputation is the surgical removal of a limb. In severe cases, foot ulcers may need to be amputated to prevent the infection from spreading. Amputation is a serious complication of diabetes, and it can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
Foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes, but they can be prevented. People with diabetes should take care of their feet by checking them daily for any injuries, wearing shoes that fit well, and keeping their blood sugar levels under control.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin, which is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy. Gestational diabetes can lead to a number of complications for both the mother and the baby, including:
- Preeclampsia: A condition that causes high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby, including seizures, stroke, and organ damage.
- Macrosomia: A condition in which the baby is born with a high birth weight. Macrosomia can increase the risk of delivery complications, such as shoulder dystocia and cesarean section.
- Hypoglycemia: A condition in which the baby’s blood sugar level drops too low. Hypoglycemia can cause seizures and other serious complications.
- Jaundice: A condition that causes the baby’s skin and whites of the eyes to turn yellow. Jaundice is caused by a build-up of bilirubin, a waste product that is produced when red blood cells are broken down.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. If you are pregnant, it is important to talk to your doctor about your risk of gestational diabetes and to follow their recommendations for managing the condition.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for over 90% of all cases. It is characterized by insulin resistance, which means that the body does not respond properly to insulin, and high blood sugar levels.
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and organs over time, leading to a number of serious complications, including:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye damage
- Nerve damage
- Foot ulcers
These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can even be life-threatening.
It is important to manage blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of developing these complications. This can be done through diet, exercise, and medication.
If you have type 2 diabetes, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that will help you keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of developing complications.
FAQs on Complications of Diabetes
Understanding the complications associated with diabetes is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Question 1: What are the most common complications of diabetes?
Diabetes can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, foot ulcers, and gestational diabetes.
Question 2: How do I know if I am at risk for developing complications from diabetes?
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels is essential for assessing your risk. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Question 3: Can complications from diabetes be prevented?
While some complications may be unavoidable, adhering to treatment plans, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk.
Question 4: What should I do if I experience any symptoms of complications?
Seek prompt medical attention if you experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, vision changes, numbness or weakness, or foot problems. Early detection and intervention are crucial.
Question 5: How often should I have my eyes and feet checked if I have diabetes?
Regular eye exams are recommended annually or as advised by your ophthalmologist. Foot examinations should be performed daily for any signs of blisters, cuts, or infections.
Question 6: What are the key lifestyle changes I can make to manage my risk of complications?
Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress are essential lifestyle modifications to minimize the risk of complications.
Remember, managing diabetes effectively requires a collaborative effort between you and your healthcare team. Open communication, regular check-ups, and adherence to treatment plans are vital in preventing or delaying the onset of complications and preserving your overall well-being.
Refer to the next section for further insights into managing diabetes and its complications.
Tips for Managing Complications of Diabetes
Effectively managing diabetes and its potential complications requires a multifaceted approach. Here are several evidence-based tips to help you navigate this journey:
Tip 1: Prioritize Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is paramount in preventing and delaying complications. Adhere to your prescribed treatment plan, including medications, insulin therapy, and lifestyle modifications to keep your blood sugar within recommended ranges.
Tip 2: Monitor Regularly
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels is crucial for early detection of any abnormalities. Home monitoring devices and regular check-ups with your healthcare team empower you with valuable data to adjust your management strategies.
Tip 3: Embrace a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive salt intake. Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and improve cardiovascular health.
Tip 4: Protect Your Feet
Diabetes can impair circulation and nerve function in the feet, increasing the risk of foot problems. Inspect your feet daily for blisters, cuts, or infections. Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes and avoid walking barefoot.
Tip 5: Quit Smoking
Smoking exacerbates cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes. Quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other vascular problems.
Tip 6: Manage Stress
Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, yoga, or meditation. Seeking professional help for stress management can be beneficial.
Tip 7: Attend Regular Eye Exams
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems. Undergo comprehensive eye exams annually or as recommended by your ophthalmologist to detect and treat any eye-related complications early on.
Tip 8: Seek Prompt Medical Attention
If you experience any symptoms of complications, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, vision changes, or numbness in your extremities, seek immediate medical attention. Early intervention can mitigate the severity of complications and improve outcomes.
Implementing these tips into your diabetes management routine empowers you to take an active role in preserving your health and well-being. Remember, consistency and adherence to these recommendations are essential for long-term success.
Conclusion
Complications of diabetes are a serious concern, as they can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. Understanding the types, causes, and preventive measures associated with these complications is crucial for individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals alike.
This article has explored the various complications of diabetes, emphasizing the importance of early detection, ongoing management, and lifestyle modifications. By adhering to treatment plans, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and adopting a balanced lifestyle, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of developing these complications and improve their overall health outcomes.
Youtube Video: