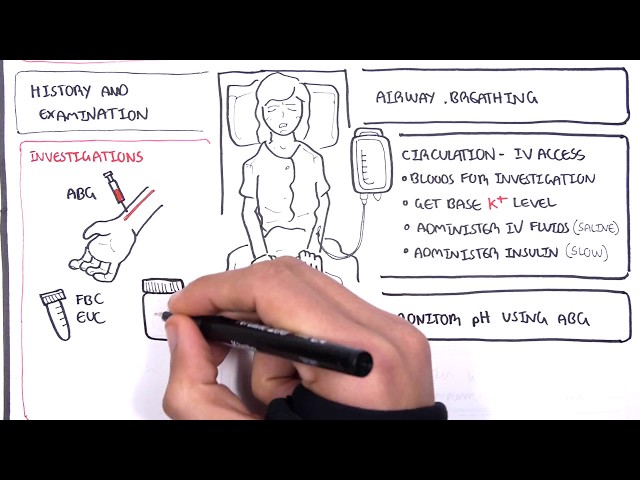
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly. Symptoms of DKA include:
- High blood sugar levels
- High levels of ketones in the blood or urine
- Dehydration
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Preventing DKA is important for people with diabetes. Ways to prevent DKA include:
- Taking insulin as prescribed
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Getting sick
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
Diabetes ketoacidosis
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Symptoms: High blood sugar, high ketones, dehydration, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, loss of consciousness
- Causes: Uncontrolled diabetes, infection, injury, surgery
- Treatment: Fluids, insulin, electrolytes
- Prevention: Taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding getting sick
- Complications: Coma, death
- Risk factors: Type 1 diabetes, poor diabetes control, history of DKA
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
Symptoms
These symptoms are all associated with diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- High blood sugar: High blood sugar is a common symptom of diabetes, and it can also be a sign of DKA. When blood sugar levels are high, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood.
- High ketones: Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Dehydration: Dehydration is a common symptom of DKA. When the body breaks down fat for energy, it produces ketones. Ketones can cause the body to lose water, which can lead to dehydration.
- Nausea and vomiting: Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of DKA. Ketones can irritate the stomach and intestines, which can cause nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal pain: Abdominal pain is a common symptom of DKA. Ketones can irritate the stomach and intestines, which can cause abdominal pain.
- Rapid breathing: Rapid breathing is a common symptom of DKA. When the body breaks down fat for energy, it produces ketones. Ketones can cause the body to lose water, which can lead to dehydration. Dehydration can cause the body to breathe more rapidly in an attempt to conserve water.
- Confusion: Confusion is a common symptom of DKA. Ketones can affect the brain, which can lead to confusion.
- Loss of consciousness: Loss of consciousness is a serious symptom of DKA. Ketones can affect the brain, which can lead to loss of consciousness.
If you have diabetes and experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a serious condition that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly.
Causes
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are not controlled. DKA is caused by a combination of factors, including uncontrolled diabetes, infection, injury, and surgery. Understanding the link between these causes and DKA is essential for effective prevention and management.
Uncontrolled diabetes is the primary cause of DKA. When blood sugar levels are not properly controlled, the body cannot use glucose for energy and begins to break down fat and muscle for energy. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and lead to DKA. Infection, injury, and surgery can also trigger DKA in people with diabetes. These events can cause stress hormones to be released, which can increase blood sugar levels and lead to DKA.
Recognizing the causes of DKA is crucial for prevention and management. People with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing DKA. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and following a healthy lifestyle. Additionally, it is important to seek medical attention promptly for any infection, injury, or surgery to prevent DKA from developing.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and managed with proper care. By understanding the causes of DKA and taking steps to prevent it, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing this life-threatening condition.
Treatment
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. The primary treatment for DKA involves the administration of fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Understanding the connection between these treatments and DKA is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Fluids are essential for treating DKA because dehydration is a common complication. When the body breaks down fat for energy, it produces ketones, which can cause the body to lose water. Dehydration can lead to a number of serious complications, including kidney failure and seizures. Insulin is another important treatment for DKA. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which can help to lower blood sugar levels and reduce the production of ketones. Electrolytes are also important for treating DKA. Electrolytes are minerals that are essential for the body’s functions, such as regulating blood pressure and muscle function. DKA can cause the body to lose electrolytes, which can lead to a number of complications, such as heart arrhythmias and muscle weakness.
The combination of fluids, insulin, and electrolytes is essential for treating DKA. These treatments help to correct dehydration, lower blood sugar levels, and restore electrolyte balance. Prompt treatment of DKA is essential to prevent serious complications and improve the chances of a full recovery.
In addition to fluids, insulin, and electrolytes, other treatments for DKA may include antibiotics if an infection is present, pain medication, and oxygen therapy. The specific treatment plan will vary depending on the individual patient’s needs.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be effectively treated with prompt and appropriate medical care. Understanding the connection between fluids, insulin, and electrolytes and DKA is essential for effective management and prevention.
Prevention
Preventing diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is crucial for individuals with diabetes. DKA is a serious complication that can occur when blood sugar levels are not properly managed. The preventive measures outlined above are essential for maintaining blood sugar control and reducing the risk of developing DKA.
Taking insulin as prescribed is essential for managing blood sugar levels in people with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which can help to prevent blood sugar levels from rising too high. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is also important for preventing DKA. By monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can identify when their blood sugar levels are rising and take steps to correct them.
Eating a healthy diet is another important aspect of preventing DKA. A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, which can help to keep blood sugar levels stable. Exercising regularly is also important for preventing DKA. Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Avoiding getting sick is also important for preventing DKA. Infection can cause blood sugar levels to rise, which can increase the risk of developing DKA.
By following these preventive measures, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing DKA. DKA is a serious complication, but it can be prevented with proper care and management.
Complications
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
-
Coma
Coma is a state of unconsciousness from which a person cannot be awakened. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including DKA. When DKA is severe, it can cause the blood to become acidic, which can lead to coma. -
Death
DKA can be fatal if not treated promptly. Even with treatment, there is a risk of death, especially if the person has other medical conditions, such as heart disease or kidney disease.
The best way to prevent DKA is to manage blood sugar levels carefully. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and eating a healthy diet. It is also important to avoid getting sick, as infection can raise blood sugar levels and increase the risk of DKA.
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications, including coma and death.
Risk factors
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are not controlled. There are a number of risk factors for DKA, including:
-
Type 1 diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes are at highest risk for DKA. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body does not produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. Without insulin, blood sugar levels can rise to dangerous levels, which can lead to DKA. -
Poor diabetes control
People with diabetes who do not control their blood sugar levels are also at risk for DKA. Poor diabetes control can be caused by a number of factors, such as not taking insulin as prescribed, not monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, or not following a healthy diet. -
History of DKA
People who have had DKA in the past are at increased risk for developing it again. This is because DKA can damage the pancreas, which is the organ that produces insulin. Damage to the pancreas can make it difficult to control blood sugar levels, which can lead to recurrent DKA.
It is important to be aware of the risk factors for DKA and to take steps to reduce your risk. If you have diabetes, it is important to take your insulin as prescribed, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, and follow a healthy diet. You should also avoid getting sick, as infection can raise blood sugar levels and increase your risk of DKA.
If you have any of the risk factors for DKA, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
FAQs on Diabetes Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of DKA?
The symptoms of DKA include:
- High blood sugar
- High levels of ketones in the blood or urine
- Dehydration
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Question 2: What causes DKA?
DKA is caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Infection
- Injury
- Surgery
Question 3: How is DKA treated?
DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Question 4: How can I prevent DKA?
You can prevent DKA by:
- Taking insulin as prescribed
- Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding getting sick
Question 5: What are the risk factors for DKA?
The risk factors for DKA include:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Poor diabetes control
- History of DKA
Question 6: What are the complications of DKA?
The complications of DKA include:
- Coma
- Death
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
If you have any other questions about DKA, please speak to your doctor or diabetes care team.
Tips for Preventing and Managing Diabetes Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. However, there are steps you can take to prevent and manage DKA.
Tip 1: Take your insulin as prescribed.
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin, and people with type 2 diabetes may not produce enough insulin. Taking insulin as prescribed can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of DKA.
Tip 2: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly can help you to identify when your blood sugar levels are rising and take steps to correct them. This can help to prevent blood sugar levels from getting too high and triggering DKA.
Tip 3: Eat a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of DKA. A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, which can help to keep blood sugar levels stable.
Tip 4: Exercise regularly.
Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This can help to reduce the risk of DKA. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 5: Avoid getting sick.
Infection can raise blood sugar levels and increase the risk of DKA. Take steps to avoid getting sick, such as washing your hands frequently, getting vaccinated, and avoiding contact with people who are sick.
Tip 6: Know the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them.
The symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar, high levels of ketones in the blood or urine, dehydration, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, and loss of consciousness. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Tip 7: Talk to your doctor or diabetes care team about DKA.
Your doctor or diabetes care team can provide you with more information about DKA, including how to prevent and manage it. They can also answer any questions you have about DKA.
Summary
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and managed. By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of developing DKA and improve your overall health.
Conclusion
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. However, there are steps you can take to prevent and manage DKA.
By following the tips outlined in this article, you can reduce your risk of developing DKA and improve your overall health. If you have any questions about DKA, please speak to your doctor or diabetes care team.
Remember, DKA is a serious condition, but it can be prevented and managed with proper care. By taking control of your diabetes, you can live a long and healthy life.
Youtube Video: