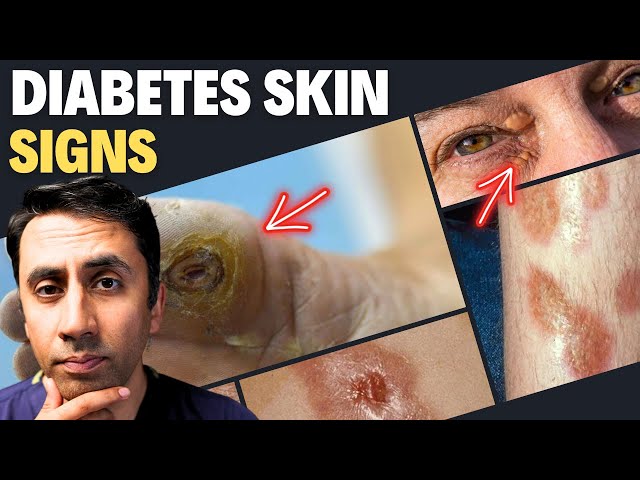
Diabetes skin is a term used to describe a range of skin conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. These conditions can include dry skin, itching, and skin infections.
Diabetes skin conditions are often caused by the high blood sugar levels that occur in people with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the skin, leading to a variety of skin problems.
Diabetes skin conditions can be a nuisance, but they can also be a sign of more serious health problems. If you have diabetes, it is important to see your doctor regularly to check for skin problems.
Diabetes Skin
Diabetes skin is a term used to describe a range of skin conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. These conditions can include dry skin, itching, and skin infections. Diabetes skin conditions are often caused by the high blood sugar levels that occur in people with diabetes.
- Symptom: Dry skin
- Symptom: Itching
- Symptom: Skin infections
- Cause: High blood sugar
- Cause: Damaged blood vessels
- Cause: Damaged nerves
- Prevention: Control blood sugar levels
- Treatment: Moisturizers, anti-itch creams, antibiotics
Diabetes skin conditions can be a nuisance, but they can also be a sign of more serious health problems. If you have diabetes, it is important to see your doctor regularly to check for skin problems. Diabetes skin conditions can often be prevented by controlling blood sugar levels. If you do develop a diabetes skin condition, there are a variety of treatments available to help relieve the symptoms.
Symptom
Dry skin is a common symptom of diabetes. It occurs when the skin does not have enough moisture. This can be caused by a number of factors, including high blood sugar levels, nerve damage, and poor circulation.
Dry skin can be a nuisance, but it can also lead to more serious problems, such as cracking, bleeding, and infection. It is important to keep the skin moisturized to prevent these complications.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat dry skin. These include:
- Controlling blood sugar levels
- Using a humidifier in the home
- Taking lukewarm baths or showers
- Applying moisturizer to the skin several times a day
If dry skin is severe, it may be necessary to see a doctor. The doctor may prescribe a topical or oral medication to help relieve the dryness.
Symptom
Itching is a common symptom of diabetes skin. It can be caused by a number of factors, including dry skin, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Itching can be a nuisance, but it can also lead to more serious problems, such as skin infections.
If you have diabetes, it is important to keep your blood sugar levels under control and to moisturize your skin regularly. This will help to prevent itching and other skin problems. If you do develop itching, there are a number of things you can do to relieve it, such as applying a cool compress, taking a lukewarm bath or shower, or using an anti-itch cream.
Symptom
Skin infections are a common complication of diabetes. They can occur when bacteria or fungi enter the skin through a break in the skin, such as a cut or scrape. People with diabetes are more likely to develop skin infections because their high blood sugar levels can damage the skin and make it more susceptible to infection.
Skin infections can be a nuisance, but they can also be serious. If left untreated, they can spread and lead to more serious health problems, such as sepsis.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat skin infections. These include:
- Controlling blood sugar levels
- Keeping the skin clean and dry
- Checking the skin regularly for any breaks or cuts
- Treating any cuts or scrapes promptly
- Taking antibiotics if prescribed by a doctor
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risk of skin infections and to take steps to prevent them. If you do develop a skin infection, it is important to see a doctor promptly so that it can be treated.
Skin infections are a serious complication of diabetes. They can be prevented by controlling blood sugar levels, keeping the skin clean and dry, and checking the skin regularly for any breaks or cuts. If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risk of skin infections and to take steps to prevent them.
Cause
High blood sugar levels are a major cause of diabetes skin problems. When blood sugar levels are high, they can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the skin. This damage can lead to a variety of skin problems, including:
- Dry skin: High blood sugar levels can cause the skin to become dry and flaky. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the skin’s natural moisture barrier.
- Itching: High blood sugar levels can also cause the skin to become itchy. This is because high blood sugar levels can irritate the nerve endings in the skin.
- Skin infections: High blood sugar levels can make the skin more susceptible to infection. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the skin’s immune system.
Controlling blood sugar levels is the best way to prevent diabetes skin problems. If you have diabetes, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that will help you keep your blood sugar levels under control.
Cause
Damaged blood vessels are a major cause of diabetes skin problems. When blood vessels are damaged, they cannot deliver oxygen and nutrients to the skin cells as effectively. This can lead to a variety of skin problems, including:
- Dry skin: Damaged blood vessels can cause the skin to become dry and flaky. This is because the skin cells are not receiving enough oxygen and nutrients to stay hydrated.
- Itching: Damaged blood vessels can also cause the skin to become itchy. This is because the damaged blood vessels release histamine, a chemical that causes itching.
- Skin infections: Damaged blood vessels can make the skin more susceptible to infection. This is because the skin cells are not receiving enough oxygen and nutrients to fight off infection.
Preventing damage to blood vessels is the best way to prevent diabetes skin problems. This can be done by controlling blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Cause
Damaged nerves are a major cause of diabetes skin problems. When nerves are damaged, they cannot send signals to the skin cells as effectively. This can lead to a variety of skin problems, including:
- Dry skin: Damaged nerves can cause the skin to become dry and flaky. This is because the nerves that control the sweat glands are damaged, and the skin cannot produce enough sweat to stay hydrated.
- Itching: Damaged nerves can also cause the skin to become itchy. This is because the damaged nerves send signals to the brain that the skin is itchy, even when it is not.
- Skin infections: Damaged nerves can make the skin more susceptible to infection. This is because the nerves that control the immune system are damaged, and the skin cannot fight off infection as effectively.
Preventing damage to nerves is the best way to prevent diabetes skin problems. This can be done by controlling blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Damaged nerves are a serious complication of diabetes. They can lead to a variety of skin problems, which can be difficult to treat. If you have diabetes, it is important to take steps to prevent nerve damage.
Prevention
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is paramount in preventing diabetes skin problems. Elevated blood sugar levels can inflict damage upon the delicate blood vessels and nerves in the skin, setting the stage for a cascade of complications.
-
Facet 1: Dry skin
Uncontrolled blood sugar wreaks havoc on the skin’s natural moisture barrier, leading to dehydration and a parched, flaky texture. This compromised barrier function increases vulnerability to external irritants and infection.
-
Facet 2: Itching
High blood sugar levels trigger the release of histamine, a chemical that incites intense itching sensations. This relentless itching can disrupt sleep, exacerbate stress levels, and further damage the skin through excessive scratching.
-
Facet 3: Skin infections
Sustained high blood sugar impairs the immune system’s ability to ward off infections, making the skin more susceptible to bacterial and fungal invasions. These infections can manifest as boils, abscesses, and cellulitis, posing a serious threat to overall health.
-
Facet 4: Nerve damage
Prolonged exposure to elevated blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage, disrupting communication between the skin and the central nervous system. This can result in impaired sensation, reduced sweating, and diminished ability to heal wounds, further exacerbating skin problems.
In summary, controlling blood sugar levels is not merely a preventive measure but a proactive strategy to safeguard the skin’s health in individuals with diabetes. By maintaining optimal glycemic control, we empower the skin to resist infection, retain moisture, and maintain its protective functions.
Treatment
To effectively manage diabetes skin problems, a multifaceted treatment approach is necessary. This involves utilizing a range of topical and oral medications to address the specific symptoms and underlying causes of the condition. Three essential categories of treatment include moisturizers, anti-itch creams, and antibiotics.
-
Moisturizers
Moisturizers are essential for replenishing the skin’s natural moisture barrier, which is often compromised in diabetes skin. By applying moisturizers regularly, the skin’s ability to retain moisture is improved, reducing dryness and flakiness. This not only enhances the skin’s appearance but also protects it from external irritants and potential infection.
-
Anti-itch Creams
Anti-itch creams provide relief from the intense itching associated with diabetes skin. These creams contain ingredients such as hydrocortisone or calamine, which help to reduce inflammation and soothe irritated skin. By controlling itching, anti-itch creams prevent further damage to the skin caused by excessive scratching, promoting healing and reducing the risk of infection.
-
Antibiotics
In cases where diabetes skin becomes infected, antibiotics are prescribed to combat the underlying bacterial or fungal infection. Antibiotics work by killing or inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, effectively clearing the infection and preventing its spread. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated.
By utilizing these treatments in combination, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their skin problems, alleviating discomfort, preventing complications, and maintaining the overall health and appearance of their skin.
FAQs on Diabetes Skin
Question 1: What causes diabetes skin problems?
Diabetes skin problems are primarily caused by elevated blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar damages blood vessels and nerves in the skin, leading to a range of skin complications.
Question 2: What are common symptoms of diabetes skin problems?
Common symptoms of diabetes skin problems include dry and flaky skin, intense itching, skin infections, and impaired wound healing. These symptoms can vary in severity and may occur in combination.
Question 3: How can I prevent diabetes skin problems?
Preventing diabetes skin problems involves managing blood sugar levels, maintaining good skin hygiene, and protecting the skin from external irritants. Regular skin examinations are also essential for early detection and treatment of any skin concerns.
Question 4: What treatments are available for diabetes skin problems?
Treatment options for diabetes skin problems include moisturizers to hydrate dry skin, anti-itch creams to alleviate itching, and antibiotics to combat infections. In severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary to manage underlying medical conditions.
Question 5: How can I care for my skin if I have diabetes?
Individuals with diabetes should follow a daily skincare routine that includes cleansing with mild soap, applying fragrance-free moisturizers, and avoiding harsh chemicals or excessive scrubbing. Regular foot examinations are crucial for preventing foot ulcers and other complications.
Question 6: When should I see a doctor about my diabetes skin problems?
It is advisable to consult a doctor if you experience persistent skin problems, such as severe itching, worsening infections, or non-healing wounds. Seeking professional medical advice ensures appropriate diagnosis and timely treatment, preventing complications.
Summary: Diabetes skin problems are common but manageable complications of diabetes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with diabetes can effectively care for their skin, prevent complications, and maintain overall skin health.
Next article section: Managing Blood Sugar Levels for Healthy Skin
Tips for Managing Diabetes Skin
Maintaining healthy skin in individuals with diabetes requires a proactive approach. Here are several essential tips to help you manage diabetes skin effectively:
Tip 1: Control Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels is paramount. Elevated blood sugar damages blood vessels and nerves in the skin, leading to a cascade of skin complications. By adhering to prescribed diabetes management plans, including medication, diet, and exercise, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of skin problems.Tip 2: Moisturize Regularly
Diabetes can cause dry, flaky skin due to impaired skin barrier function. Using fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers helps replenish and protect the skin’s natural moisture. Apply moisturizer liberally and frequently, especially after bathing or showering, to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.Tip 3: Manage Itching
Itching is a common and often bothersome symptom of diabetes skin. Avoid scratching, as this can damage the skin and increase the risk of infection. Instead, use topical anti-itch creams or lotions containing hydrocortisone or calamine to soothe irritated skin and reduce itching sensations.Tip 4: Treat Infections Promptly
Diabetes impairs the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to skin infections. If you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, or drainage, seek medical attention promptly. Early treatment with antibiotics or antifungal medications can effectively clear the infection and prevent complications.Tip 5: Practice Good Foot Care
Foot problems are a common complication of diabetes. Inspect your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or sores. Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes and socks to prevent friction and pressure. Keep your feet clean and dry, and trim your toenails regularly to maintain good foot health.Tip 6: Avoid Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs circulation, which can worsen diabetes skin problems. Quitting smoking is crucial for overall health and can significantly improve skin health in individuals with diabetes.Tip 7: Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate diabetes skin problems. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, yoga, or meditation to manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.Summary: By following these tips, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their skin health, reduce the risk of complications, and maintain the overall appearance and function of their skin.
Next article section: The Importance of Skin Care in Diabetes Management
Conclusion
Diabetes skin problems are a common and often overlooked complication of diabetes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with diabetes can effectively care for their skin, prevent complications, and maintain overall skin health.
Managing diabetes skin requires a multifaceted approach that includes controlling blood sugar levels, practicing good skin hygiene, using appropriate skincare products, and seeking medical attention for any skin concerns. By following these strategies, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their skin health, improve their quality of life, and reduce the risk of serious complications.
Remember, healthy skin is an essential component of overall well-being in individuals with diabetes. By prioritizing skin care and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can achieve optimal skin health and live full and active lives.
Youtube Video: