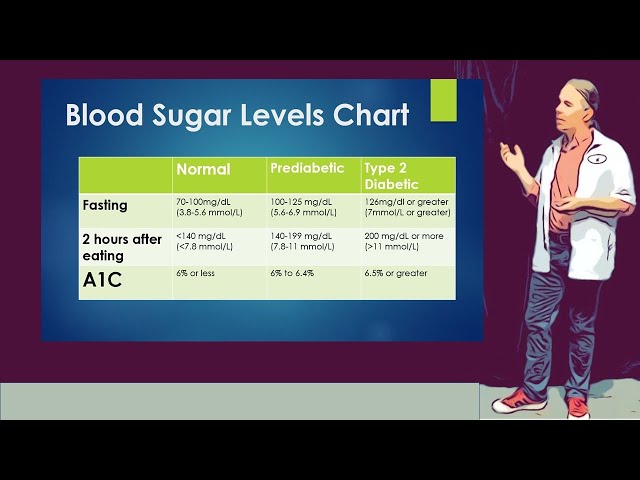
Diabetic levels after eating refer to the glucose levels in the bloodstream of a person with diabetes after they have eaten. For people without diabetes, blood sugar levels typically rise after eating and then return to normal within a few hours. However, for people with diabetes, their bodies are unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels, which can lead to high levels of glucose in the bloodstream after eating.
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves over time, leading to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Therefore, it is important for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and to take steps to keep them within a healthy range. This may involve taking medication, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
If you have diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about how to manage your blood sugar levels. They can provide you with personalized advice and support to help you stay healthy.
Diabetic levels after eating
Understanding diabetic levels after eating is crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. Here are 8 key aspects to consider:
- Blood glucose monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels after eating helps manage diabetes effectively.
- Carbohydrate counting: Understanding the impact of different carbohydrates on blood sugar levels is essential.
- Insulin therapy: For some individuals, insulin may be necessary to regulate blood sugar levels after meals.
- Exercise: Physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels after eating.
- Meal planning: Planning meals that include a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fat can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Fiber intake: Soluble fiber can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after eating.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help the body flush out excess glucose.
- Long-term effects: Consistently high blood sugar levels after eating can increase the risk of developing diabetes complications.
By understanding and managing these key aspects, individuals with diabetes can better control their blood sugar levels after eating, reducing the risk of complications and improving their overall health and well-being.
Blood glucose monitoring
Regularly checking blood sugar levels after eating is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes effectively. By monitoring blood glucose levels, individuals can understand how their body responds to different foods and activities, allowing them to make informed choices to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring patterns: Blood glucose monitoring helps identify patterns in blood sugar levels, enabling individuals to adjust their diet, medication, or physical activity accordingly.
- Medication management: Monitoring blood sugar levels after eating can help determine the effectiveness of diabetes medications, allowing healthcare professionals to make necessary adjustments to the dosage or type of medication.
- Dietary modifications: By understanding how specific foods impact blood sugar levels, individuals can make informed dietary choices to minimize spikes and maintain stable blood sugar levels after eating.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Blood glucose monitoring can provide insights into the impact of exercise, stress, or other lifestyle factors on blood sugar levels, empowering individuals to make positive lifestyle adjustments for better diabetes management.
In conclusion, regular blood glucose monitoring after eating is essential for effective diabetes management. By providing valuable data on blood sugar patterns, medication effectiveness, dietary choices, and lifestyle factors, blood glucose monitoring empowers individuals to make informed decisions and work with their healthcare team to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
Carbohydrate counting
Carbohydrate counting is a fundamental aspect of diabetes management, as it helps individuals understand how different carbohydrates affect their blood sugar levels. This knowledge is crucial for managing diabetic levels after eating, as carbohydrates are the primary nutrient that raises blood sugar levels.
- Glycemic index (GI): The GI measures how quickly carbohydrates are broken down and absorbed into the bloodstream, influencing the rate at which blood sugar levels rise. High-GI carbohydrates cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, while low-GI carbohydrates result in a more gradual rise, making them a better choice for people with diabetes.
- Glycemic load (GL): The GL considers both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates consumed. It provides a more accurate estimate of the impact of a particular food on blood sugar levels, as it takes into account the serving size.
- Fiber content: Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is not digested by the body. It can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after eating.
- Types of carbohydrates: There are three main types of carbohydrates: sugars, starches, and fiber. Sugars are simple carbohydrates that are quickly absorbed and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Starches are complex carbohydrates that are broken down more slowly, resulting in a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Fiber, as mentioned earlier, does not raise blood sugar levels.
By understanding the impact of different carbohydrates on blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can make informed choices about the foods they eat. This knowledge empowers them to manage their diabetic levels after eating more effectively, reducing the risk of complications and improving their overall health and well-being.
Insulin therapy
Insulin therapy is a crucial component of managing diabetic levels after eating for individuals whose bodies do not produce enough insulin or do not use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, enter cells for energy production. Without adequate insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
When blood sugar levels rise after eating, the pancreas typically releases insulin to facilitate the absorption of glucose into cells. However, in individuals with diabetes, this process may be impaired, resulting in high blood sugar levels after meals. Insulin therapy helps to regulate these levels by providing the necessary insulin to transport glucose into cells, effectively lowering blood sugar levels.
The use of insulin therapy can significantly improve blood sugar control, reducing the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. It allows individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels more effectively, enabling them to enjoy a better quality of life.
Exercise
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in managing diabetic levels after eating. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin and improving glucose uptake into muscles. This process allows the body to utilize glucose more effectively, resulting in lower blood sugar levels.
- Enhanced insulin sensitivity: Exercise increases the number of insulin receptors on cells, making them more responsive to insulin. As a result, insulin can work more effectively to transport glucose into cells, reducing blood sugar levels.
- Improved glucose uptake: Physical activity stimulates the translocation of glucose transporter proteins to the muscle cell membrane. These proteins facilitate the entry of glucose into muscle cells, where it can be used for energy production, further lowering blood sugar levels.
- Increased muscle mass: Regular exercise helps build muscle mass, which is metabolically active and requires glucose for energy. Increased muscle mass leads to greater glucose utilization, contributing to lower blood sugar levels after eating.
- Reduced inflammation: Exercise has anti-inflammatory effects, which can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Chronic inflammation is linked to insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels, so exercise can help counteract these effects.
Incorporating regular physical activity into a diabetes management plan is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels after eating. Exercise not only helps lower blood sugar levels but also provides numerous other health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Meal planning
Meal planning is a crucial aspect of managing diabetic levels after eating as it directly influences the body’s glucose response. When meals are balanced in terms of carbohydrates, protein, and fat, the body is able to process and utilize glucose more effectively, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body, and when consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. A sudden influx of glucose can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, especially if the meal is high in refined carbohydrates. Protein and fat, on the other hand, slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing sharp increases in blood sugar levels. Additionally, protein and fat promote satiety, helping individuals feel fuller for longer and reducing the likelihood of overeating and subsequent blood sugar spikes.
In practice, meal planning for stable blood sugar levels involves choosing foods from all, and paying attention to portion sizes. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide a steadier source of glucose compared to refined carbohydrates. Lean protein sources, such as fish, chicken, and beans, help slow down digestion and promote satiety. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, olive oil, and nuts, also contribute to blood sugar stability. By incorporating these principles into meal planning, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels after eating.
Fiber intake
Soluble fiber plays a crucial role in managing diabetic levels after eating by slowing down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. This process helps prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar levels that can occur after consuming sugary foods or refined carbohydrates. When soluble fiber is consumed, it forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, which traps sugar molecules and delays their absorption. This slower absorption rate allows the body to process glucose more gradually, resulting in more stable blood sugar levels.
The importance of soluble fiber in managing diabetic levels after eating is significant. By slowing down sugar absorption, soluble fiber helps prevent the post-meal blood sugar spikes that can contribute to long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Additionally, soluble fiber promotes satiety and fullness, which can help individuals with diabetes manage their weight and reduce their overall food intake, further contributing to blood sugar control.
Incorporating soluble fiber into the diet is a practical and effective way to manage diabetic levels after eating. Good sources of soluble fiber include oats, barley, beans, lentils, apples, bananas, and carrots. By including these foods in meals and snacks, individuals with diabetes can benefit from the blood sugar-stabilizing effects of soluble fiber.
Hydration
Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for managing diabetic levels after eating. When blood sugar levels rise after a meal, the body draws water from tissues to dilute the glucose in the bloodstream. Drinking plenty of water helps replenish these fluids and promotes the excretion of excess glucose through urine.
- Improved Glucose Filtration: Ample hydration enhances the kidneys’ ability to filter glucose from the blood. The increased urine output helps eliminate excess glucose, preventing its accumulation in the bloodstream.
- Reduced Dehydration: Dehydration can worsen hyperglycemia by concentrating blood glucose levels. Staying hydrated helps maintain proper blood volume and prevents dehydration, which can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Appetite Control: Drinking water before and after meals can promote satiety and reduce overall food intake. This can help prevent overeating and excessive calorie consumption, factors that can contribute to high blood sugar levels.
- Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity: Studies suggest that good hydration may improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more effectively in transporting glucose into cells. This can further help lower blood sugar levels.
In summary, maintaining adequate hydration through sufficient water intake plays a vital role in managing diabetic levels after eating. By promoting glucose excretion, reducing dehydration, controlling appetite, and potentially improving insulin sensitivity, hydration supports the body’s natural mechanisms for regulating blood sugar levels.
Long-term effects
Chronically elevated blood sugar levels after eating, referred to as diabetic levels after eating, pose a significant threat to an individual’s health and well-being. Over time, consistently high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to severe complications that affect various organs and systems in the body.
One of the primary concerns associated with diabetic levels after eating is the increased risk of developing microvascular complications, which affect small blood vessels. These complications include:
- Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to vision impairment or blindness.
- Nephropathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the kidneys, which can impair kidney function and lead to kidney failure.
- Neuropathy: Damage to the nerves, often causing numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands and feet.
Diabetic levels after eating can also contribute to macrovascular complications, which affect large blood vessels. These complications include:
- Cardiovascular disease: Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- Cerebrovascular disease: Increased risk of stroke due to damage to blood vessels in the brain.
Understanding the long-term effects of consistently high blood sugar levels after eating is essential for individuals with diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adherence to a comprehensive diabetes management plan, including medication, diet, and exercise, are crucial in preventing or delaying the onset of these complications. By effectively managing diabetic levels after eating, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these severe health conditions and maintain their overall well-being.
FAQs about Diabetic Levels After Eating
Diabetic levels after eating refer to the blood glucose levels in the bloodstream of a person with diabetes after they have eaten. To help you understand this subject better, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions and their respective answers.
Question 1: What causes high blood sugar levels after eating?
Elevated blood sugar levels after eating can be attributed to several factors. These include the consumption of foods high in carbohydrates, inadequate insulin production or resistance to insulin’s effects, and delayed gastric emptying.
Question 2: How can I lower my blood sugar levels after eating?
Effective strategies to reduce blood sugar levels after eating involve engaging in physical activity, consuming foods rich in fiber, spacing out carbohydrate intake, managing stress levels, and ensuring adequate hydration.
Question 3: What are the risks associated with consistently high blood sugar levels after eating?
Sustained high blood sugar levels after eating can lead to severe health complications, including damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs. These complications can manifest as retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, cardiovascular disease, and cerebrovascular disease.
Question 4: How can I prevent high blood sugar levels after eating?
Preventive measures to avoid elevated blood sugar levels after eating include regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to a balanced diet plan, engaging in regular physical activity, taking prescribed medications as directed, and managing stress levels.
Question 5: When should I seek medical attention for high blood sugar levels after eating?
If you experience persistent high blood sugar levels after eating, accompanied by symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, blurred vision, or fatigue, prompt medical attention is advised.
Question 6: How can I manage my diabetic levels after eating effectively?
Effective management of diabetic levels after eating involves a comprehensive approach that includes regular blood sugar monitoring, dietary modifications, medication adherence, physical activity, stress management, and regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Summary: Understanding and managing diabetic levels after eating is crucial for individuals with diabetes. By implementing the strategies outlined in this FAQ section, you can effectively lower and maintain healthy blood sugar levels after eating, reducing the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
Transition to the next article section: For further insights and guidance on managing diabetic levels after eating, please refer to the following article sections.
Tips for Managing Diabetic Levels After Eating
Effectively managing diabetic levels after eating is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Implementing these practical tips can help you maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
Tip 1: Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Regular blood glucose monitoring allows you to track your blood sugar levels before and after meals. This information helps you identify patterns, adjust your insulin doses if necessary, and make informed dietary choices.
Tip 2: Choose Foods Low in Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which can raise blood sugar levels. Opt for foods lower in carbohydrates, such as non-starchy vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats, to avoid significant blood sugar spikes.
Tip 3: Include Fiber in Your Diet
Fiber helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Incorporate soluble fiber from sources like oats, beans, and apples into your meals.
Tip 4: Engage in Physical Activity
Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to use insulin more effectively. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 5: Take Your Medications as Prescribed
If you are prescribed insulin or other blood sugar-lowering medications, take them exactly as directed. These medications can help regulate your blood sugar levels and prevent spikes after eating.
Tip 6: Manage Stress Levels
Stress can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature to keep your stress levels in check.
Tip 7: Get Enough Sleep
Lack of sleep can impair insulin sensitivity and increase blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to support healthy blood sugar management.
Tip 8: Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess glucose from your body and prevents dehydration, which can contribute to high blood sugar levels.
Summary: Managing diabetic levels after eating is essential for long-term health. By following these tips, you can effectively control your blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall well-being.
Diabetic Levels After Eating
In conclusion, understanding and managing diabetic levels after eating is paramount for individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar levels after eating can lead to severe complications, including damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, you can effectively control your blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of these complications, and maintain your overall health and well-being.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adherence to a balanced diet, engagement in physical activity, and proper medication management are crucial aspects of managing diabetic levels after eating. By working closely with your healthcare provider and following their guidance, you can successfully manage your diabetes and live a healthy, fulfilling life.
Youtube Video: