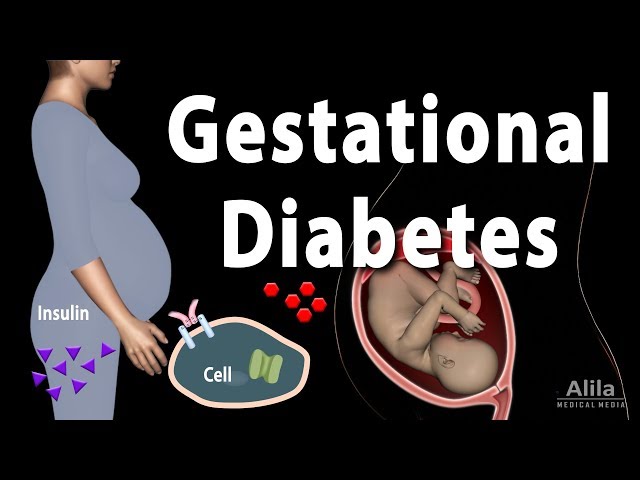
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. Due to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, it can cause high blood sugar levels. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Anyone can develop gestational diabetes, but some people are at higher risk, including those who are overweight or obese before pregnancy, have a family history of diabetes, or are over the age of 25.
It is crucial to manage pregnancy diabetes to avoid complications for both the mother and the baby. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise. In some cases, medication may also be necessary. By following these steps, you can help reduce the risks associated with pregnancy diabetes and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
If you are pregnant, talk to your doctor about your risk of developing gestational diabetes. They can recommend ways to prevent or manage the condition and help you have a healthy pregnancy.
Pregnancy Diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It requires careful management to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby. Key aspects of pregnancy diabetes include:
- Gestational: Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
- Blood sugar: Pregnancy diabetes causes high blood sugar levels.
- Risks: Pregnancy diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Management: Pregnancy diabetes can be managed through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Complications: Unmanaged pregnancy diabetes can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby.
- Prevention: There are steps that can be taken to prevent pregnancy diabetes, such as maintaining a healthy weight before pregnancy and eating a healthy diet.
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By understanding the key aspects of pregnancy diabetes, you can help reduce the risks associated with the condition and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Gestational
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is caused by hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, which can make it difficult for the body to use insulin effectively. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can be harmful to both the mother and the baby. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Causes: Gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. These hormones can make it difficult for the body to use insulin effectively, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms: Gestational diabetes often does not cause any symptoms, but some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Risks: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It can also lead to complications during pregnancy, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and macrosomia (a large baby).
- Treatment: Gestational diabetes can be managed through diet, exercise, and medication. Treatment aims to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and risks of gestational diabetes, you can help reduce the risks associated with the condition and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Blood sugar
Blood sugar levels are an essential component of pregnancy diabetes. During pregnancy, the body produces hormones that can make it difficult for the body to use insulin effectively. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can be harmful to both the mother and the baby. High blood sugar levels can cause the baby to grow too large, which can lead to complications during delivery. It can also increase the risk of premature birth and other health problems for the baby.
It is important to manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy to avoid these complications. This can be done through diet, exercise, and medication. A healthy diet for pregnancy diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit sugar and processed foods. Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Medication may be necessary if diet and exercise are not enough to control blood sugar levels.
Managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy is essential for the health of both the mother and the baby. By understanding the connection between blood sugar levels and pregnancy diabetes, you can help reduce the risks associated with the condition and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Risks
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This is because pregnancy diabetes can damage the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. When the pancreas is damaged, it cannot produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and type 2 diabetes.
There are a number of factors that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes after pregnancy diabetes, including:
- Being overweight or obese before pregnancy
- Having a family history of diabetes
- Being over the age of 25
- Having gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
If you have pregnancy diabetes, it is important to take steps to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This includes:
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication if necessary
By following these steps, you can help reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes after pregnancy diabetes.
Understanding the connection between pregnancy diabetes and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life is important for women who have had pregnancy diabetes. By taking steps to reduce their risk, women can help improve their long-term health and well-being.
Management
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. However, it can be managed through diet, exercise, and medication. These three components work together to help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
- Diet: A healthy diet for pregnancy diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit sugar and processed foods. Eating a healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
- Exercise: Exercise is another important part of managing pregnancy diabetes. Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy.
- Medication: Medication may be necessary if diet and exercise are not enough to control blood sugar levels. There are a number of different medications that can be used to treat pregnancy diabetes. Your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you.
By following these three steps, you can help to manage your pregnancy diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. It is important to work closely with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Complications
Unmanaged pregnancy diabetes can lead to a number of serious complications for both the mother and the baby. These complications can include:
- Pre-eclampsia: Pre-eclampsia is a pregnancy complication that is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby, including stroke, kidney failure, and seizures.
- Premature birth: Premature birth is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of gestation. Babies who are born prematurely are at risk for a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and learning disabilities.
- Macrosomia: Macrosomia is a condition in which a baby is born with a birth weight of more than 9 pounds, 15 ounces. Babies with macrosomia are at risk for a number of health problems, including birth injuries, obesity, and diabetes.
- Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is a condition in which a baby’s blood sugar levels drop too low. Hypoglycemia can lead to seizures, coma, and even death.
These are just some of the many complications that can occur as a result of unmanaged pregnancy diabetes. It is important to manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy to reduce the risk of these complications and ensure the health of both the mother and the baby.
Prevention
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. However, there are steps that can be taken to prevent pregnancy diabetes, such as maintaining a healthy weight before pregnancy and eating a healthy diet.
Maintaining a healthy weight before pregnancy can help to reduce the risk of pregnancy diabetes. This is because being overweight or obese can increase the risk of insulin resistance, which is a condition that can lead to pregnancy diabetes. Eating a healthy diet can also help to reduce the risk of pregnancy diabetes. A healthy diet for pregnancy includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit sugar and processed foods.
By following these steps, women can help to reduce their risk of developing pregnancy diabetes and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Preventing pregnancy diabetes is important for the health of both the mother and the baby. By understanding the connection between prevention and pregnancy diabetes, women can take steps to reduce their risk of developing this condition.
FAQs on Pregnancy Diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to understand the risks, symptoms, and treatment options for pregnancy diabetes in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and the baby. Here are some frequently asked questions about pregnancy diabetes:
Question 1: What is pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by hormonal changes that make it difficult for the body to use insulin effectively, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Question 2: What are the risks of pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and the baby. It can also lead to complications during pregnancy, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and macrosomia (a large baby).
Question 3: What are the symptoms of pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes often does not cause any symptoms, but some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Question 4: How is pregnancy diabetes treated?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes can be managed through diet, exercise, and medication. Treatment aims to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Question 5: Can pregnancy diabetes be prevented?
Answer: There are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of pregnancy diabetes, such as maintaining a healthy weight before pregnancy and eating a healthy diet.
Question 6: What is the long-term outlook for women with pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Most women with pregnancy diabetes will deliver healthy babies and go on to have normal pregnancies in the future. However, women with pregnancy diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, so it is important to follow up with their doctor after pregnancy to manage their risk.
Summary: Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to understand the risks, symptoms, and treatment options for pregnancy diabetes in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and the baby.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on pregnancy diabetes, please visit the following resources:
Tips for Managing Pregnancy Diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy to avoid complications for both the mother and the baby. Here are five tips for managing pregnancy diabetes:
Tip 1: Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet for pregnancy diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit sugar and processed foods. Eating a healthy diet can help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Tip 2: Get regular exercise. Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy.
Tip 3: Monitor your blood sugar levels. Monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential for managing pregnancy diabetes. Your doctor will recommend how often you should check your blood sugar levels.
Tip 4: Take medication if necessary. Medication may be necessary if diet, exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels are not enough to control blood sugar levels. Your doctor will prescribe the best medication for you.
Tip 5: Follow your doctor’s advice. It is important to follow your doctor’s advice on managing pregnancy diabetes. Your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Summary: By following these tips, you can help to manage your pregnancy diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. It is important to work closely with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Managing pregnancy diabetes can be challenging, but it is important to remember that you are not alone. There are many resources available to help you manage your condition and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Conclusion
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to understand the risks, symptoms, and treatment options for pregnancy diabetes in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and the baby. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help to manage your pregnancy diabetes and reduce the risk of complications.
If you have any questions or concerns about pregnancy diabetes, please talk to your doctor. They can provide you with the best medical advice for your individual situation.
Youtube Video: