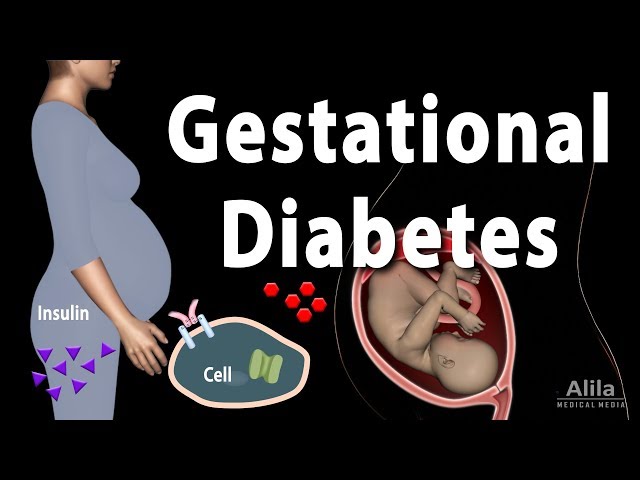
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Gestational diabetes can also cause problems for your baby, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and breathing problems.
If you have gestational diabetes, you will need to monitor your blood sugar levels and make changes to your diet and exercise routine. You may also need to take medication to help control your blood sugar levels. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your gestational diabetes and protect your health and the health of your baby.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life and protect your baby from health problems.
What Happens if You Have Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to be aware of the risks and complications associated with gestational diabetes so that you can take steps to manage your condition and protect your health and the health of your baby.
- High blood sugar levels
- Insulin resistance
- Preeclampsia
- Cesarean delivery
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Breathing problems
- Type 2 diabetes
Gestational diabetes can also increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications.
By understanding the risks and complications associated with gestational diabetes, you can take steps to protect your health and the health of your baby.
High blood sugar levels
High blood sugar levels are a hallmark of gestational diabetes. When you have gestational diabetes, your body does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that helps glucose (sugar) get from your blood into your cells for energy. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause a number of problems for you and your baby.
-
Increased risk of preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby, including premature birth, low birth weight, and even death. -
Increased risk of cesarean delivery
High blood sugar levels can also increase your risk of needing a cesarean delivery. This is because high blood sugar levels can make it difficult for your baby to tolerate labor. -
Increased risk of premature birth
High blood sugar levels can also increase your risk of premature birth. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the placenta, which is the organ that provides oxygen and nutrients to your baby. -
Increased risk of low birth weight
High blood sugar levels can also increase your risk of having a low birth weight baby. This is because high blood sugar levels can restrict the growth of your baby.
High blood sugar levels during pregnancy can also increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond normally to insulin, a hormone that helps glucose (sugar) get from the blood into the cells for energy. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause a number of problems for you and your baby during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that can make the body more resistant to insulin. This is normal and helps to ensure that your baby gets the glucose it needs to grow and develop. However, in some women, the body becomes too resistant to insulin, which can lead to gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes can increase your risk of developing a number of serious health problems, including:
- Preeclampsia
- Cesarean delivery
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Breathing problems
- Type 2 diabetes
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Insulin resistance is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on your health and the health of your baby during pregnancy. By understanding the risks and complications associated with insulin resistance, you can take steps to protect your health and the health of your baby.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby, including premature birth, low birth weight, and even death.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Gestational diabetes can also cause problems for your baby, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and breathing problems.
There is a strong link between gestational diabetes and preeclampsia. Women with gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing preeclampsia, and women with preeclampsia are at an increased risk of having a baby with gestational diabetes. This is because both conditions are caused by problems with the placenta, the organ that provides oxygen and nutrients to the baby during pregnancy.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risks of preeclampsia and to monitor your blood pressure and urine protein levels closely. If you develop any symptoms of preeclampsia, such as high blood pressure, swelling in your hands and face, or changes in your vision, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Preeclampsia is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help reduce your risk of developing preeclampsia and protect your health and the health of your baby.
Cesarean delivery
Cesarean delivery, also known as a C-section, is a surgical procedure to deliver a baby through an incision in the abdomen and uterus. It is typically performed when vaginal delivery is not possible or safe. Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of cesarean delivery for a number of reasons.
-
Macrosomia
Gestational diabetes can lead to macrosomia, a condition in which the baby is born with a high birth weight. Macrosomia can make vaginal delivery difficult or impossible, increasing the need for a cesarean delivery. -
Shoulder dystocia
Shoulder dystocia is a condition in which the baby’s shoulders become stuck during delivery. This can be a serious complication, and it is more likely to occur in babies with macrosomia. Cesarean delivery is often necessary to prevent shoulder dystocia in babies with gestational diabetes. -
Placental abruption
Placental abruption is a condition in which the placenta separates from the uterus before delivery. This can be a life-threatening complication for both the mother and the baby. Gestational diabetes is a risk factor for placental abruption, and it can increase the need for a cesarean delivery. -
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Gestational diabetes is a risk factor for preeclampsia, and preeclampsia can increase the need for a cesarean delivery.
Cesarean delivery is a major surgery, and it is important to weigh the risks and benefits before making a decision. If you have gestational diabetes, your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of cesarean delivery with you and help you make the best decision for you and your baby.
Premature birth
Premature birth is a serious complication of gestational diabetes. It occurs when a baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation. Babies born prematurely are at an increased risk of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
- Gestational diabetes increases the risk of premature birth by two to four times. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the placenta, which is the organ that provides oxygen and nutrients to the baby. A damaged placenta can lead to premature birth.
- Premature babies are more likely to have respiratory problems. This is because their lungs are not fully developed and may not be able to function properly on their own. Respiratory problems can lead to serious health complications, such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
- Premature babies may have difficulty feeding. This is because they may not be able to suck or swallow properly. Feeding difficulties can lead to malnutrition and dehydration.
- Premature babies may have developmental delays. This is because their brains are not fully developed and may not be able to function properly. Developmental delays can affect a child’s physical, cognitive, and social development.
Premature birth is a serious complication of gestational diabetes, but it can be prevented. By managing your blood sugar levels and following your doctor’s instructions, you can help reduce your risk of premature birth and protect your baby’s health.
Low birth weight
Low birth weight is a serious complication of gestational diabetes. It occurs when a baby is born weighing less than 2,500 grams (5 pounds, 8 ounces). Babies with low birth weight are at an increased risk of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
- Gestational diabetes increases the risk of low birth weight by two to four times. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the placenta, which is the organ that provides oxygen and nutrients to the baby. A damaged placenta can restrict the baby’s growth, leading to low birth weight.
- Babies with low birth weight are more likely to have respiratory problems. This is because their lungs are not fully developed and may not be able to function properly on their own. Respiratory problems can lead to serious health complications, such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
- Babies with low birth weight may have difficulty feeding. This is because they may not be able to suck or swallow properly. Feeding difficulties can lead to malnutrition and dehydration.
- Babies with low birth weight may have developmental delays. This is because their brains are not fully developed and may not be able to function properly. Developmental delays can affect a child’s physical, cognitive, and social development.
Low birth weight is a serious complication of gestational diabetes, but it can be prevented. By managing your blood sugar levels and following your doctor’s instructions, you can help reduce your risk of low birth weight and protect your baby’s health.
Breathing problems
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Gestational diabetes can also cause problems for your baby, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and breathing problems.
-
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS is a condition that can occur in premature babies when their lungs are not fully developed. It can cause difficulty breathing and may require oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
-
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTN)
TTN is a common breathing problem in newborns that usually goes away on its own within a few days. It is caused by fluid in the baby’s lungs that is not absorbed quickly enough.
-
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)
BPD is a chronic lung disease that can develop in premature babies who have needed mechanical ventilation for a long period of time. It can cause scarring of the lungs and difficulty breathing.
-
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It can be a serious complication of gestational diabetes, especially in premature babies.
Breathing problems are a serious complication of gestational diabetes, but they can be prevented or treated. By managing your blood sugar levels and following your doctor’s instructions, you can help reduce your risk of breathing problems and protect your baby’s health.
Type 2 diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which your body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause a number of health problems.
-
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which your body’s cells do not respond normally to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes can increase your risk of developing insulin resistance later in life.
-
Obesity
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can increase your risk of becoming obese later in life.
-
Physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is another major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can make it more difficult to be physically active, which can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
-
Family history of diabetes
If you have a family history of diabetes, you are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can further increase your risk.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
FAQs
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Gestational diabetes can also cause problems for your baby, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and breathing problems.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of gestational diabetes?
Many women with gestational diabetes do not have any symptoms. However, some women may experience the following symptoms:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Frequent infections
Question 2: How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test. This test is usually done between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. The test involves drinking a sugary drink and then having your blood sugar levels checked at regular intervals.
Question 3: How is gestational diabetes treated?
Gestational diabetes is treated with diet, exercise, and medication. Your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Question 4: Can gestational diabetes be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Managing your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes
Question 5: What are the risks of gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can increase your risk of developing the following problems:
- Preeclampsia
- Cesarean delivery
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Breathing problems
- Stillbirth
Question 6: What happens after I have my baby if I had gestational diabetes?
After you have your baby, your blood sugar levels will usually return to normal. However, you will need to continue to monitor your blood sugar levels and follow your doctor’s instructions to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on your health and the health of your baby. By understanding the risks and complications associated with gestational diabetes, you can take steps to protect your health and the health of your baby.
Transition to the next article section:
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Tips for Managing Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on your health and the health of your baby. By following these tips, you can help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Tip 1: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
This will help you to identify any patterns in your blood sugar levels and make adjustments to your diet and exercise plan as needed.
Tip 2: Eat a healthy diet.
Focus on eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit your intake of sugary drinks and processed foods.
Tip 3: Get regular exercise.
Exercise can help to lower your blood sugar levels and improve your overall health.
Tip 4: Take medication if prescribed by your doctor.
If your blood sugar levels cannot be controlled with diet and exercise alone, your doctor may prescribe medication to help you manage your blood sugar levels.
Tip 5: Attend prenatal appointments regularly.
Your doctor will monitor your blood sugar levels and check for any complications.
Tip 6: Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Your doctor will provide you with specific instructions on how to manage your gestational diabetes. It is important to follow these instructions carefully to help reduce your risk of complications.
Tip 7: Take care of your mental health.
Gestational diabetes can be a stressful condition. It is important to take care of your mental health by getting enough sleep, eating healthy foods, and exercising regularly.
Tip 8: Join a support group.
Connecting with other women who have gestational diabetes can provide you with support and encouragement.
By following these tips, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications. Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By working closely with your doctor and following these tips, you can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
If you have any questions or concerns about gestational diabetes, please talk to your doctor.
Conclusion
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on the health of both the mother and the baby. By understanding the risks and complications associated with gestational diabetes, you can take steps to protect your health and the health of your baby.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications. By working closely with your doctor and following the tips outlined in this article, you can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Youtube Video: