Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes, a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Regular blood sugar checks provide valuable information about how well your diabetes management plan is working and can help prevent or minimize complications.
Regular blood sugar monitoring can help people with diabetes:
- Assess the effectiveness of their diabetes management plan
- Identify patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels
- Detect and prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)
- Adjust insulin doses or medications as needed
- Reduce the risk of long-term complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness
There are several methods for monitoring blood sugar levels, including using a glucometer, continuous glucose monitor (CGM), or a blood test at a doctor’s office. The appropriate method will depend on individual needs and preferences. Regular blood sugar monitoring is an essential aspect of diabetes management and can significantly improve health outcomes for those living with this condition.
sugar level reading for diabetes
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications. Key aspects of sugar level reading for diabetes include:
- Frequency: How often blood sugar levels should be checked
- Timing: When blood sugar levels should be checked, such as before meals or at bedtime
- Method: The method used to check blood sugar levels, such as a glucometer or CGM
- Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy of blood sugar readings
- Interpretation: Understanding what blood sugar readings mean
- Action: Taking appropriate action based on blood sugar readings, such as adjusting insulin doses or medications
- Communication: Sharing blood sugar readings with healthcare providers
These aspects are interconnected and essential for effective diabetes management. For example, frequent and accurate blood sugar readings allow individuals to identify patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels. This information can help them make informed decisions about their diabetes management plan and reduce the risk of complications. Regular communication with healthcare providers is also crucial, as they can provide guidance on interpreting blood sugar readings and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Frequency
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring is a crucial aspect of effective diabetes management. Regular checks provide valuable information about blood sugar patterns and trends, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes care.
The optimal frequency of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual factors such as the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and blood sugar control. However, general guidelines recommend that people with diabetes check their blood sugar levels:
- Before meals: To determine the appropriate insulin dose
- 2 hours after meals: To assess how well the body is responding to insulin and to identify any post-meal blood sugar spikes
- At bedtime: To prevent nocturnal hypoglycemia
- At other times as needed: Such as when experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to identify patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels. This information can help them adjust their insulin doses or medications, as well as make lifestyle changes to improve their blood sugar control. Frequent blood sugar checks can also help prevent or minimize complications by detecting and addressing blood sugar fluctuations promptly.
Timing
The timing of blood sugar checks is crucial for effective diabetes management. Checking blood sugar levels at specific times provides valuable information about how the body is responding to insulin and helps individuals make informed decisions about their diabetes care.
Before meals: Checking blood sugar levels before meals helps determine the appropriate dose of insulin. This is especially important for people who take insulin before meals to control their blood sugar levels.
2 hours after meals: Checking blood sugar levels 2 hours after meals helps assess how well the body is responding to insulin and to identify any post-meal blood sugar spikes. This information can help adjust insulin doses or medications to prevent or minimize blood sugar fluctuations.
At bedtime: Checking blood sugar levels at bedtime helps prevent nocturnal hypoglycemia, a condition that occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low during the night. Nocturnal hypoglycemia can be dangerous and may lead to seizures or loss of consciousness.
Regular blood sugar monitoring at the appropriate times is essential for effective diabetes management. By understanding the connection between timing and blood sugar levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diabetes care and reduce the risk of complications.
Method
The method used to check blood sugar levels plays a crucial role in the accuracy and effectiveness of sugar level reading for diabetes. Two common methods are glucometers and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
Glucometers are small, portable devices that measure blood sugar levels from a drop of blood obtained by pricking the finger. They provide a quick and convenient way to check blood sugar levels at home or on the go. However, glucometers require manual testing, which can be inconvenient and painful for some individuals.
CGMs are small, wearable devices that continuously monitor blood sugar levels through a sensor inserted under the skin. They provide real-time data on blood sugar trends and fluctuations, which can be particularly useful for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those who experience frequent blood sugar variability. CGMs eliminate the need for finger pricks and provide more comprehensive data, but they are more expensive and may not be suitable for everyone.
Choosing the appropriate method for checking blood sugar levels depends on individual needs and preferences. Glucometers are generally more affordable and convenient for occasional blood sugar checks, while CGMs offer more comprehensive data and can be beneficial for individuals requiring close monitoring of their blood sugar levels.
Accuracy
Accurate blood sugar readings are essential for effective diabetes management, as they provide reliable information for making informed decisions about insulin doses, medications, and lifestyle choices. Several factors contribute to the accuracy of blood sugar readings, including:
- Proper technique: Using the correct technique when checking blood sugar levels is crucial. This includes washing hands, using a clean lancet, and applying the blood sample correctly to the test strip.
- Calibration: Glucometers need to be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate readings. This involves using a control solution to check the accuracy of the meter.
- Test strip quality: Using high-quality test strips is important for accurate readings. Expired or damaged test strips can provide inaccurate results.
- Interfering substances: Certain substances, such as vitamin C, can interfere with blood sugar readings. It is important to be aware of potential interfering substances and take steps to minimize their impact.
Inaccurate blood sugar readings can lead to incorrect treatment decisions, which can have serious consequences for individuals with diabetes. Therefore, it is essential to ensure the accuracy of blood sugar readings by following proper technique, calibrating glucometers regularly, using high-quality test strips, and being aware of potential interfering substances.
Interpretation
Interpreting blood sugar readings is a crucial aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. Accurately understanding the meaning of blood sugar readings empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their diabetes management and reduce the risk of complications.
- Target blood sugar ranges: Healthcare providers establish target blood sugar ranges for each individual based on factors such as age, type of diabetes, and overall health. Understanding these target ranges helps individuals assess whether their blood sugar readings are within the desired levels.
- Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia: Blood sugar readings can indicate whether an individual is experiencing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Recognizing the symptoms and appropriate actions for both conditions is essential to prevent or manage these blood sugar extremes.
- Patterns and trends: Monitoring blood sugar readings over time allows individuals to identify patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels. This information can help them understand how different factors, such as diet, exercise, and medications, affect their blood sugar control.
- Adjusting treatment plans: Interpreting blood sugar readings is essential for adjusting insulin doses, medications, or lifestyle choices to optimize blood sugar control. Regular monitoring and interpretation of blood sugar readings empower individuals to take an active role in managing their diabetes.
Understanding what blood sugar readings mean is fundamental to effective diabetes management. By interpreting blood sugar readings accurately, individuals can make informed decisions, prevent complications, and improve their overall health outcomes.
Action
Taking appropriate action based on blood sugar readings is a crucial component of sugar level reading for diabetes. By monitoring blood sugar levels and understanding what the readings mean, individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions to manage their condition effectively.
The most common action based on blood sugar readings is adjusting insulin doses or medications. When blood sugar levels are high, individuals may need to increase their insulin dose or take additional medication to lower their blood sugar. Conversely, when blood sugar levels are low, they may need to decrease their insulin dose or take glucose to raise their blood sugar.
Taking appropriate action based on blood sugar readings is essential for preventing and managing complications of diabetes. High blood sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Low blood sugar levels can also be dangerous, causing seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death if not treated promptly.
By understanding the connection between blood sugar readings and appropriate actions, individuals with diabetes can take an active role in managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications. Regular blood sugar monitoring and prompt action based on the readings are essential for maintaining good blood sugar control and overall health.
Communication
Effective communication between individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers is a crucial component of successful diabetes management. Sharing blood sugar readings with healthcare providers allows them to assess blood sugar control, identify patterns and trends, and make informed decisions about treatment plans.
Regularly sharing blood sugar readings with healthcare providers helps them:
- Monitor blood sugar control over time
- Identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels
- Detect and prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)
- Adjust insulin doses or medications as needed
- Identify and address any underlying issues affecting blood sugar control
For example, if an individual with diabetes consistently experiences high blood sugar readings before breakfast, their healthcare provider may recommend adjusting their insulin dose or taking additional medication. Conversely, if an individual experiences frequent hypoglycemia, their healthcare provider may reduce their insulin dose or recommend lifestyle changes to improve blood sugar control.
Open and regular communication between individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers is essential for effective diabetes management. Sharing blood sugar readings is a vital part of this communication, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment plans and individuals to take an active role in managing their condition.
FAQs on Sugar Level Reading for Diabetes
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for effective diabetes management and prevention of complications. Here are answers to some commonly asked questions about sugar level reading for diabetes:
Question 1: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
The frequency of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual factors, but general guidelines recommend checking before meals, 2 hours after meals, at bedtime, and at other times as needed, such as when experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
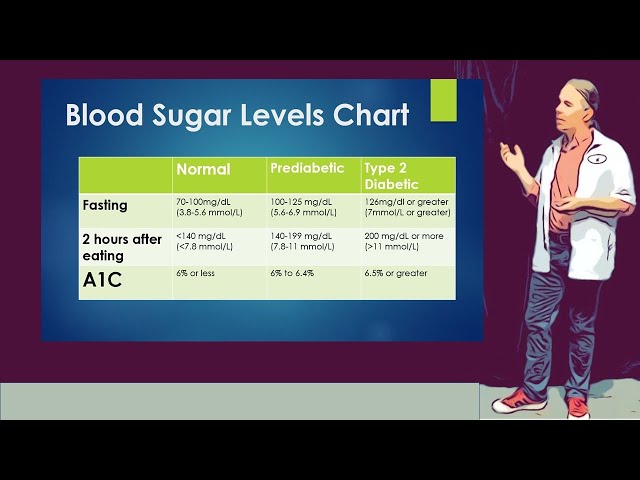
Question 2: What is a normal blood sugar range?
Target blood sugar ranges may vary depending on individual circumstances, but typical ranges are: Before meals: 80-130 mg/dL (4.4-7.2 mmol/L), 2 hours after meals: Less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L), At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL (5.6-7.8 mmol/L).
Question 3: What should I do if my blood sugar is too high?
If your blood sugar is high, you may need to increase your insulin dose or take additional medication. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice on adjusting your treatment plan.
Question 4: What should I do if my blood sugar is too low?
If your blood sugar is low, you should consume a source of glucose, such as juice or candy, to raise your blood sugar levels. It is important to carry a fast-acting source of glucose with you in case of hypoglycemia.
Question 5: How can I improve the accuracy of my blood sugar readings?
To ensure accurate readings, use the correct technique, calibrate your glucometer regularly, use high-quality test strips, and be aware of potential interfering substances.
Question 6: How often should I share my blood sugar readings with my healthcare provider?
Regularly sharing your blood sugar readings with your healthcare provider is essential for monitoring your blood sugar control, identifying patterns, and making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Effective blood sugar monitoring and interpretation are crucial for diabetes management. By understanding these key aspects, individuals with diabetes can take an active role in controlling their blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding the Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Tips for Effective Blood Sugar Monitoring in Diabetes Management
Regular and accurate blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management. Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your blood sugar readings:
Tip 1: Check your blood sugar regularly.
The frequency of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual factors, but general guidelines recommend checking before meals, 2 hours after meals, at bedtime, and at other times as needed, such as when experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Tip 2: Use a high-quality blood glucose meter.
The accuracy of your blood sugar readings depends on the quality of your meter. Choose a meter that is accurate, easy to use, and fits your lifestyle.
Tip 3: Calibrate your meter regularly.
All blood glucose meters require calibration to ensure accurate readings. Calibrate your meter according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Tip 4: Use the correct technique.
Proper technique is crucial for accurate blood sugar readings. Wash your hands thoroughly, use a clean lancet, and apply the blood sample correctly to the test strip.
Tip 5: Be aware of potential interfering substances.
Certain substances, such as vitamin C and certain medications, can interfere with blood sugar readings. Be aware of these substances and take steps to minimize their impact.
Tip 6: Keep a log of your readings.
Tracking your blood sugar readings over time can help you identify patterns and trends. This information can be valuable for you and your healthcare provider when making decisions about your diabetes management plan.
Summary: By following these tips, you can ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of your blood sugar readings. Regular and accurate blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management and prevention of complications.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Conclusion
Regular and accurate blood sugar monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. By understanding the importance of sugar level reading, individuals with diabetes can take an active role in controlling their blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications.
This article has explored the key aspects of sugar level reading for diabetes, including frequency, timing, method, accuracy, interpretation, action, and communication. By following the tips and guidelines provided, individuals with diabetes can ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of their blood sugar readings. This information empowers them to make informed decisions about their diabetes management plan and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
Youtube Video: